What are White Patches?
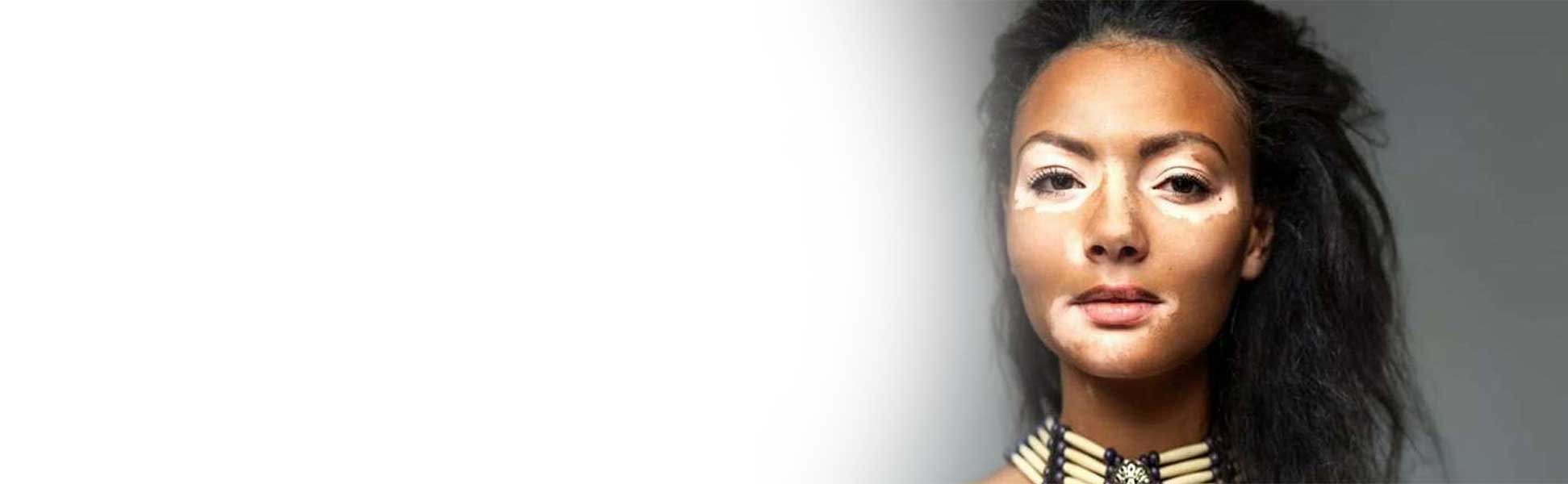
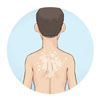
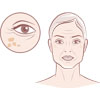
White patches, also known clinically as Vitiligo, is the result of lacking melanin in the skin. Melanin is the protein present in the skin cells (Melanocytes) that gives every individual their respective skin color. When the affliction to vitiligo is observed, the general conclusion is that there are not enough working melanocytes to produce enough melanin in the skin. This causes white patches to appear and seemingly spread or grow across the skin and even sometimes hair.
This is a skin condition that has led to the stigmatization of an individual’s appearance, which is responsible for a gross marginalization of people with the condition. This leads to insecurities about their appearance due to their ill treatment in society.
Types of Vitiligo:
-
Focal Vitiligo: Where the white patches are clustered in one area, such as arms legs, back or face.
-
Generalized Vitiligo: Where the individual has white patches all over the body and usually affects them in a symmetrical pattern. This is the most common type of Vitiligo.
-
Segmental Vitiligo: Where the individual has vitiligo patches on only one area of the body. Least common type.
What Causes Vitiligo ?
As stated above, the main cause for vitiligo is the low performance of melanocytes in the skin. Though there is no discernible evidence as to what exactly causes vitiligo, the theory that autoimmune disorders are partly responsible gains merit under the assumption that the immune system attacks the healthy skin cells resulting in melanin reduction. Many researchers believe that it is also a genetic condition.
However there are many factors that could possibly trigger the failure of melanocytes. One possible condition is related to a history of Autoimmune disorders. It can also happen anywhere on the body and usually appears in areas with heavy sun exposure.
It is also largely believed that Vitiligo is triggered by stressful events, severe skin damage due to sun burns, chemical burns, cuts, etc. It is also heavily misunderstood as being contagious. You cannot contract Vitiligo from an individual who has it, neither is it caused by any bateria, virus or infection.
What are the Risk Factors or Complications due to Vitiligo ?
Vitiligo can usually lead to vulnerabilities in the skin and increase the susceptibility to skin conditions more. Due to decreased melanin, people with vitiligo are more prone to skin cancers and sunburns due to minor exposures to sun.
There is also some evidence that suggests the linking of eye and ear problems, such as iris inflammation, inflammation of the middle layer of the eye and even partial loss of hearing.
What is the possible treatment?
Though there is no cure for Vitiligo, there are treatment options to reduce their appearance. For example, a skin camouflage, with appropriate cosmetic merit can be used to cover up small and visible spots. Some mild steroid creams are available that can restore a certain amount of color to the skin, but can have severe side effects such as sagging, stretch marks, skin thinning, etc. In some cases, phototherapy may be used to restore skin color, however they are not very effective and are costly. Treatment is not known to stop the spreading of this condition.
The most effective coping mechanism comes from dealing with the social stigma and self esteem issues caused by it, which can be handled with the help of support groups and mental health specialists. Creating awareness about Vitiligo must be the first step to understanding and removing the misconceptions and misunderstandings.