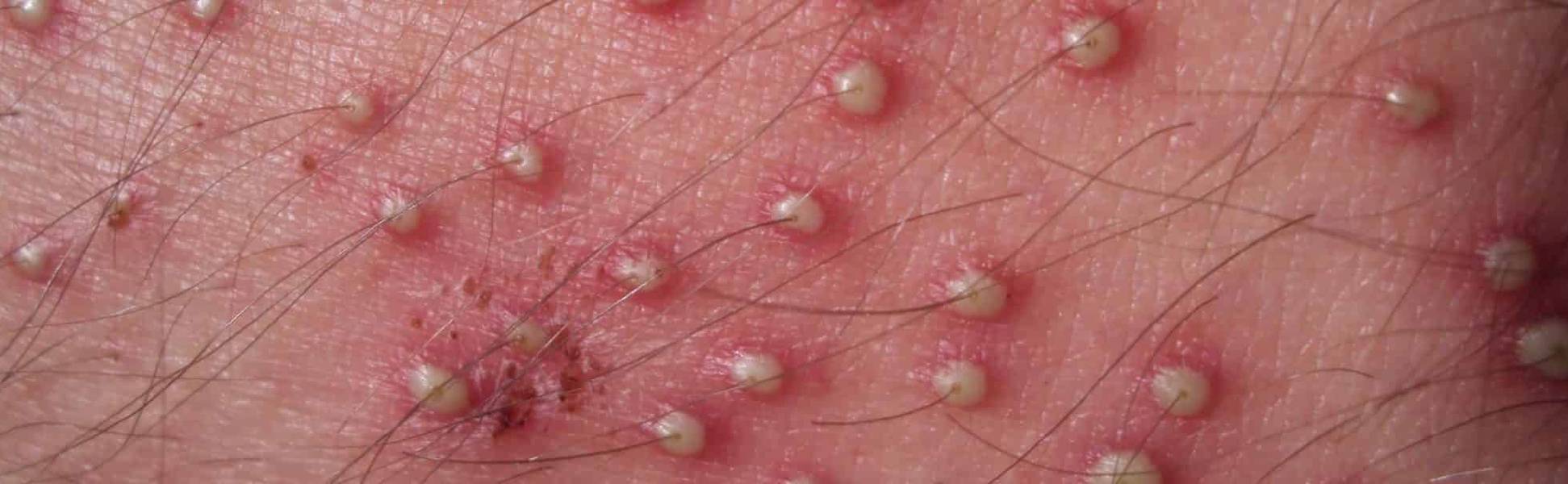
Folliculitis is a common skin condition characterized by inflammation of one or more hair follicles due to infection. Folliculitis appears in the form of itchy, sore small red bumps, sometimes white pus-filled tips and crust around the infected follicle. The crusty non-healing sores look like acne or pimples.
While folliculitis appears on any part of the body, it commonly affects the arms, legs, buttocks, genitals, chest, back, head, and face.
Although folliculitis is not a life-threatening condition chronic folliculitis can be uncomfortable, embarrassing, scarring and may cause permanent hair loss. However, mild folliculitis can be cured eventually by just basic self-care measures. While the chronic condition requires physicians' help.
Pathogenesis of folliculitis:
Both acute and chronic conditions can be caused due to bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic infection. The noninfectious etiologies sometimes play a role in the pathophysiology such as follicular trauma, inflammation, or occlusion due to any physical means. In many of the cases, the cause remains idiopathic. The pathophysiology of folliculitis involves acneiform eruption secondary to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. However, the underlying mechanism is poorly understood. As per one hypothesis, the mechanism behind the papulopustular eruption secondary to the inhibition of follicular epidermal differentiation is follicular obstruction and subsequent inflammation. The eosinophilic folliculitis has different pathophysiology than other types of folliculitis. It occurs due to autoimmunity against the sebocytes or components of the sebum.
The predisposing factors of folliculitis include decreased immunity, skin injury, staphylococcal carrier status, malnutrition, diabetes, obesity, occlusion caused by topical products, medications (topical and systemic steroids, lithium, contraceptive agents, antiepileptics, epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors, and long-term use of antibiotics), poorly chlorinated hot tubs, and actinic damage, hair follicle damage due to shaving of curly hair, waxing, wearing tight clothing, or clothing that traps heat and sweat.
Symptoms of folliculitis
The common signs and symptoms of folliculitis are:
- Clusters of small red bumps or white-tip pimples around hair follicles
- Pus-filled blisters that break open and crust over
- Itchy bumps causing burning sensation
- Painful and tender
- Large swollen bumps or masses
Complications
The complications of folliculitis include:
- Recurrent infection
- Permanent skin damage, such as scarring or dark spots
- Destruction of hair follicles and permanent hair loss
Hence, to prevent infection one should take the following measures:
- Avoid tight clothing
- Person with razor bumps should avoid shaving
- Use of clean hot tubs and heated pools
- Judicious use of skin oils and other greasy skin products, as they can cause blockages and trap bacteria
- Shave with care even though not having prior razor bumps
- Use of clean towels, napkins
- Take care of personal hygiene
Diagnosis
The doctor can diagnose the condition by closely observing the affected area, checking disease history. The doctor may perform a microscopic examination by a dermoscope. If the infection did not cure after initial treatment, the swab of infected skin or follicle is taken for laboratory investigation. Skin biopsy is rarely required.